第三部分 第九章 2.字节流
条评论9.2 字节流
9.2.1 一切皆为字节
一切文件数据(文本、图片、视频等)在存储时,都是以二进制数字的形式保存,都一个一个的字节,那么传输时一样如此。所以,字节流可以传输任意文件数据。在操作流的时候,我们要时刻明确,无论使用什么样的流对象,底层传输的始终为二进制数据。
9.2.2 字节输出流【OutputStream】
java.io.OutputStream抽象类是表示字节输出流的所有类的超类,将指定的字节信息写出到目的地。它定义了字节输出流的基本共性功能方法。
public void close():关闭此输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源。public void flush():刷新此输出流并强制任何缓冲的输出字节被写出。public void write(byte[] b):将 b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此输出流。public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len):从指定的字节数组写入 len字节,从偏移量 off开始输出到此输出流。public abstract void write(int b):将指定的字节输出流。小贴士:
close()方法,当完成流的操作时,必须调用此方法,释放系统资源。
9.2.3 FileOutputStream类
OutputStream有很多子类,我们从最简单的一个子类开始。
java.io.FileOutputStream 类是文件输出流,用于将数据写出到文件。
构造方法
public FileOutputStream(File file):创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。public FileOutputStream(String name):创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。
当你创建一个流对象时,必须传入一个文件路径。该路径下,如果没有这个文件,会创建该文件。如果有这个文件,会清空这个文件的数据。
构造举例,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public class FileOutputStreamConstructor throws IOException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用File对象创建流对象
File file = new File("a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("b.txt");
}
}
写出字节数据
写出字节:
write(int b)方法,每次可以写出一个字节数据,代码使用演示:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public class FOSWrite {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt");
// 写出数据
fos.write(97); // 写出第1个字节
fos.write(98); // 写出第2个字节
fos.write(99); // 写出第3个字节
// 关闭资源
fos.close();
}
}1
2文件内容:
abc小贴士:
1、虽然参数为int类型的四个字节,但是只会保留一个字节的信息写出。
2、流操作完毕后,必须释放系统资源,调用close方法,千万记得。写出字节数组:
write(byte[] b),每次可以写出数组中的数据,代码使用演示:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public class FOSWrite {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt");
// 字符串转换为字节数组
byte[] b = "字符串转换为字节数组".getBytes();
// 写出字节数组数据
fos.write(b);
// 关闭资源
fos.close();
}
}1
2文件内容:
字符串转换为字节数组写出指定长度字节数组:
write(byte[] b, int off, int len),每次写出从off索引开始,len个字节,代码使用演示:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public class FOSWrite {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt");
// 字符串转换为字节数组
byte[] b = "abcde".getBytes();
// 写出从索引2开始,2个字节。索引2是c,两个字节,也就是cd。
fos.write(b,2,2);
// 关闭资源
fos.close();
}
}1
2文件内容:
cd
数据追加续写
经过以上的演示,每次程序运行,创建输出流对象,都会清空目标文件中的数据。如何保留目标文件中数据,还能继续添加新数据呢?
public FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append):创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。public FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append):创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。
这两个构造方法,参数中都需要传入一个boolean类型的值, true表示追加数据, false表示清空原有数据。
这样创建的输出流对象,就可以指定是否追加续写了,代码使用演示:
1 | public class FOSWrite { |
1 | 文件操作前:cd |
写出换行
Windows系统里,换行符号是\r\n。把
以指定是否追加续写了,代码使用演示:
1 | public class FOSWrite { |
1 | 输出结果: |
- 回车符
\r和换行符\n**:
- 回车符:回到一行的开头(return)。
- 换行符:下一行(newline)。
- 系统中的换行:
- Windows系统里,每行结尾是
回车+换行,即\r\n;- Unix系统里,每行结尾只有
换行,即\n;- Mac系统里,每行结尾是
回车,即\r。从 Mac OS X开始与Linux统一。
9.2.4 字节输入流【InputStream】
java.io.InputStream抽象类是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类,可以读取字节信息到内存中。它定义了字节输入流的基本共性功能方法。
public void close():关闭此输入流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源。public abstract int read():从输入流读取数据的下一个字节。public int read(byte[] b):从输入流中读取一些字节数,并将它们存储到字节数组 b中 。小贴士:
close()方法,当完成流的操作时,必须调用此方法,释放系统资源。
9.2.5 FileInputStream类
java.io.FileInputStream类是文件输入流,从文件中读取字节。
构造方法
FileInputStream(File file):通过打开与实际文件的连接来创建一个FileInputStream,该文件由文件系统中的File对象 file 命名。FileInputStream(String name):通过打开与实际文件的连接来创建一个FileInputStream,该文件由文件系统中的路径名 name 命名。
当你创建一个流对象时,必须传入一个文件路径。该路径下,如果没有该文件,会抛出FileNotFoundException。
构造举例,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public class FileInputStreamConstructor throws IOException{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用File对象创建流对象
File file = new File("a.txt");
FileInputStream fos = new FileInputStream(file);
// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileInputStream fos = new FileInputStream("b.txt");
}
}
读取字节数据
读取字节:
read方法,每次可以读取一个字节的数据,提升为int类型,读取到文件末尾,返回-1,代码使用演示:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public class FISRead {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt");
// 读取数据,返回一个字节
int read = fis.read();
System.out.println((char) read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println((char) read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println((char) read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println((char) read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println((char) read);
// 读取到末尾,返回‐1
read = fis.read();
System.out.println( read);
// 关闭资源
fis.close();
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7输出结果:
a
b
c
d
e
‐1循环改进读取方式,代码使用演示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public class FISRead {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt");
// 定义变量,保存数据
int b ;
// 循环读取
while ((b = fis.read())!=‐1) {
System.out.println((char)b);
}
// 关闭资源
fis.close();
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6输出结果:
a
b
c
d
e小贴士:
1、虽然读取了一个字节,但是会自动提升为int类型。
2、流操作完毕后,必须释放系统资源,调用close方法,千万记得。使用字节数组读取:
read(byte[] b),每次读取b的长度个字节到数组中,返回读取到的有效字节个数,读取到末尾时,返回-1,代码使用演示:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18public class FISRead {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// 使用文件名称创建流对象.
// 文件中为abcde
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt");
// 定义变量,作为有效个数
int len;
// 定义字节数组,作为装字节数据的容器
byte[] b = new byte[2];
// 循环读取
while (( len= fis.read(b))!=‐1) {
// 每次读取后,把数组变成字符串打印
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
// 关闭资源
fis.close();
}
}1
2
3
4输出结果:
ab
cd
ed错误数据
d,是由于最后一次读取时,只读取一个字节e,数组中,上次读取的数据没有被完全替换,所以要通过len,获取有效的字节,代码使用演示:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19public class FISRead {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// 使用文件名称创建流对象.
// 文件中为abcde
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt");
// 定义变量,作为有效个数
int len;
// 定义字节数组,作为装字节数据的容器
byte[] b = new byte[2];
// 循环读取
while (( len= fis.read(b))!=‐1) {
// 每次读取后,把数组的有效字节部分,变成字符串打印
// len 每次读取的有效字节个数
System.out.println(new String(b,0,len));
}
// 关闭资源
fis.close();
}
}1
2
3
4输出结果:
ab
cd
e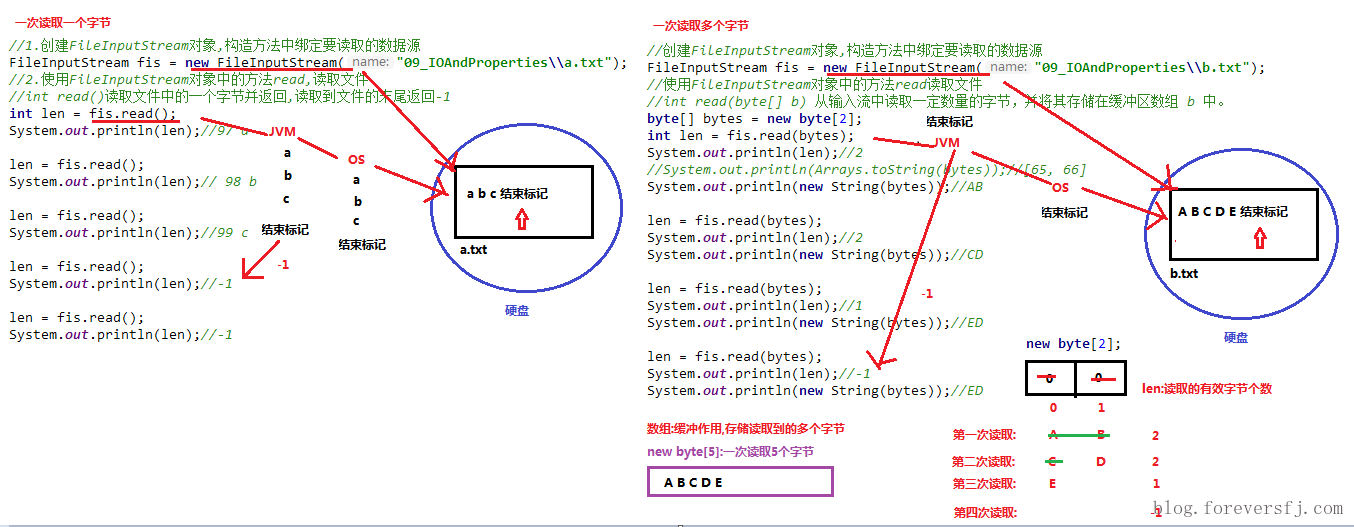
小贴士:
使用数组读取,每次读取多个字节,减少了系统间的IO操作次数,从而提高了读写的效率,建议开发中使用。
9.2.6 字节流练习:图片复制
复制原理图解
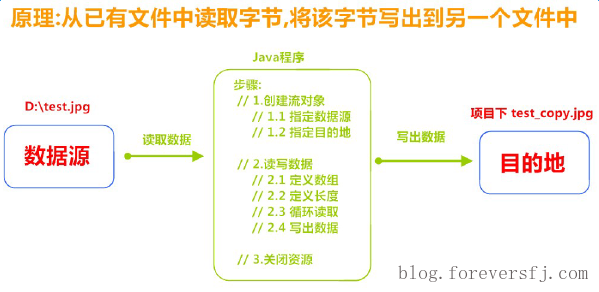
案例实现
- 复制图片文件,代码使用演示:
1 | public class Copy { |
小贴士:
流的关闭原则:先开后关,后开先关。
本文标题:第三部分 第九章 2.字节流
文章作者:foreverSFJ
发布时间:2019-08-20 21:35:38
最后更新:2019-08-20 21:35:38
原始链接:Notes/Java/Basic/Part03/09_2 字节流.html
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
分享
